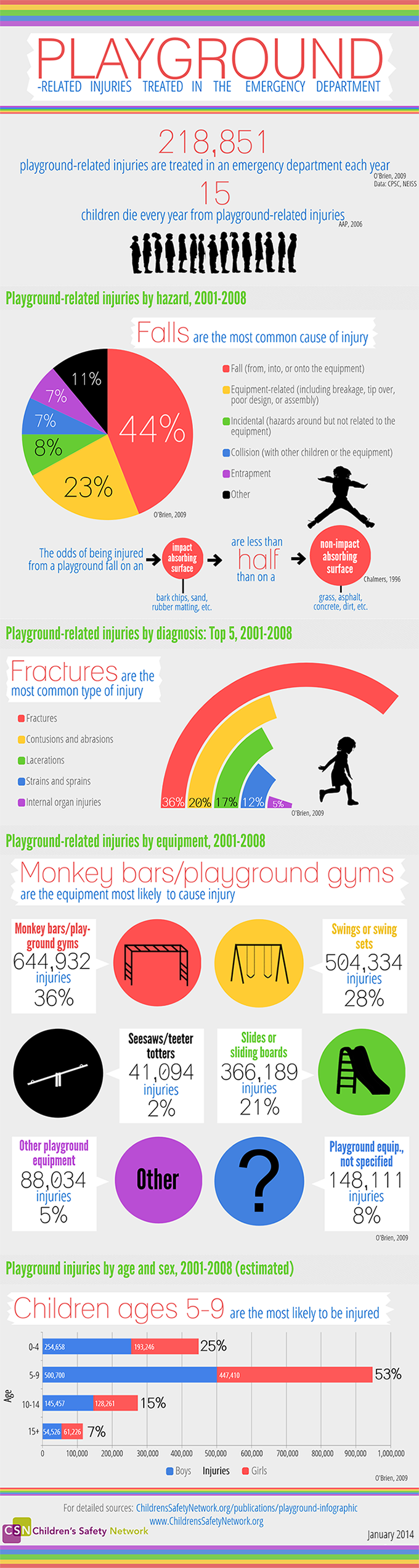
218,851 playground-related injuries are treated in an emergency department each year. This infographic breaks down playground-related injuries by hazard, diagnosis, equipment, and age and sex. Additional resources on playground safety can be found in the text below.
For more information about playground safety, visit:
Playground Safety resources from CPSC
Caring for Our Children: National Health and Safety Performance Standards Guidelines for Early Care and Education Programs, 3rd Edition from the National Resource Center for Health and Safety in Child Care and Early Education (NRC)
The National Program for Playground Safety from the University of Northern Iowa
Playground-Related Injuries Treated in the Emergency Department
218,851 playground-related injuries are treated in an emergency department each year (O’Brien, 2009)
15 children die every year from playground-related injuries (American Academy of Pediatrics, 2006)
Playground-related injuries by hazard, 2001-1008
Falls were the most common cause of injury (O’Brien, 2009)
|
Hazard |
Percent |
|
Fall (from, into, or onto the equipment) |
44% |
|
Equipment-related (including breakage, tip over, poor design, or assembly) |
23% |
|
Incidental (hazards around but not related to the equipment) |
8% |
|
Collision (with other children or the equipment) |
7% |
|
Entrapment |
7% |
|
Other |
11% |
The odds of being injured from a playground fall on an impact absorbing surface (bark chips, sand, rubber matting/tiles) are less than half than on a non-impact absorbing surface (grass, asphalt, concrete) (Chalmers et al., 1996)
Playground-related injuries by diagnosis: Top 5, 2001-1008
Fractures were the most common type of injury (O’Brien, 2009)
|
Diagnosis |
Percent |
|
Fractures |
36% |
|
Contusions and abrasions |
20% |
|
Lacerations |
17% |
|
Strains and sprains |
12% |
|
Internal organ injuries |
5% |
Playground-related injuries by equipment, 2001-1008
Monkey bars/playground gyms are the equipment most likely to cause injury (O’Brien, 2009)
|
Equipment type |
Total injuries |
Percent |
|
Monkey bars or playground gyms |
644932 |
36% |
|
Swings or swing sets |
504334 |
28% |
|
Slides or sliding boards |
366189 |
21% |
|
Playground equipment, not specified |
148111 |
8% |
|
Other playground equipment |
88034 |
5% |
|
Seesaws or teeter totters |
41094 |
2% |
Playground-related injuries by age and sex, 2001-1008
Children ages 5-9 are the most likely to be injured (O’Brien, 2009)
|
Age |
Male (total injuries) |
Female (total injuries) |
Total percent |
|
0-4 |
254658 |
193246 |
25% |
|
5-9 |
500700 |
447410 |
53% |
|
10-11 |
145457 |
128261 |
15% |
|
15+ |
54526 |
61226 |
7% |
Sources
American Academy of Pediatrics. (2006). Playground Safety. Patient Education Online. Retrieved from http://patiented.aap.org/content2.aspx?aid=5689&refURL=
Chalmers, D. J., Marshall, S. W., Langley, J. D., Evans, M. J., Brunton, C. R., Kelly, a M., & Pickering, a F. (1996). Height and surfacing as risk factors for injury in falls from playground equipment: a case-control study. Injury prevention : journal of the International Society for Child and Adolescent Injury Prevention, 2(2), 98–104. Retrieved from http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1067669&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
O’Brien, C. W. (2009). Injuries and Investigated Deaths Associated with Playground Equipment, 2001-2008 (Vol. 280, p. 24). Bethesda, MD. doi:10.1111/febs.12425. Retrieved from: http://www.cpsc.gov/PageFiles/108596/playground.pdf