CSN Fact Sheets, Reports and Issue Briefs
![]() This page displays all Children’s Safety Network (CSN) Fact Sheets, Reports, and Issue Briefs. Please feel free to download and share through Facebook, X, Pinterest, or email.
This page displays all Children’s Safety Network (CSN) Fact Sheets, Reports, and Issue Briefs. Please feel free to download and share through Facebook, X, Pinterest, or email.
Released Date:
Released Date:
Childhood lays the foundation for future success, with safe and supportive environments promoting healthier adult outcomes. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) can lead to long-term social, behavioral, and health challenges. Preventing and addressing ACEs is vital, and requires family, community,…
Released Date:
Youth who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, questioning, or other non-heterosexual identity (LGBQ+) are resilient1 and diverse, representing every racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic group and are present in every community across the U.S.2 They make up 24% of the high-school aged population.3…
Released Date:
Youth who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, questioning, or other non-heterosexual identity (LGBQ+) are resilient1 and diverse, representing every racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic group and are present in every community across the U.S.2 They make up 24% of the high-school aged population.3…
Released Date:
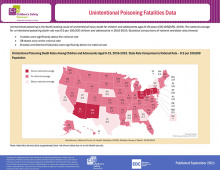
In 2020, unintentional poisoning was the second leading cause of unintentional injury deaths for children and adolescents ages 1-19. Drug poisoning was related to 73% of the unintentional poisoning deaths in children ages 0-9, and 96% of the unintentional poisoning deaths in adolescents ages 10-19…
Released Date:
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be mild, moderate or severe. It is defined as a disruption in the normal functioning of the brain due to a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or a penetrating head injury.1 It is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the U.S. that can have life-long financial,…
Released Date:
Adolescence is a time when many young people start their first romantic relationships. Dating can be a new and exciting phase in teens’ lives that helps them learn more about themselves and sets the stage for future relationships. But for many teens, the dating experience can also include different…
Released Date:
Injuries and violence are among the most serious social, economic, medical, and public health issues. Injuries and violence are a leading killer among all ages, and the number one killer among kids, teens, and adults ages 1-44.1 Injuries and violence affect all of us including the families left…
Released Date:
When a disaster, disease outbreak, or other crisis occurs, overwhelming a community’s capacity to respond, child safety efforts often need to adapt in order to be sustained. These disruptions can increase the risk for child injury and illness, while also creating serious challenges for…
Released Date:
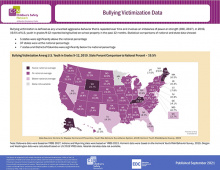
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Bullying Victimization.
Released Date:
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Unintentional Poisoning Fatalities.
Released Date:
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Adolescent Suicide Deaths.
Released Date:
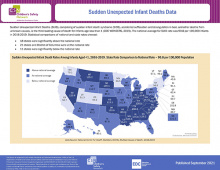
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths.
Released Date:
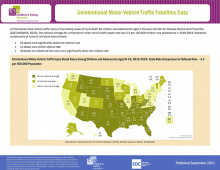
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Unintentional Motor Vehicle Traffic Fatalities.
Released Date:
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Bullying Victimization, Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths,…
Released Date:
The Planner is for use at the departmental and/or programmatic/work unit level to assess integration of integrative approaches in child safety initiatives. The Planner may be used as a stand-alone tool or with the CSN Framework for Quality Improvement and Innovation in Child Safety: A Guide to…
Released Date:
Suicide is a complex and preventable multi-factor, multi-level health outcome. Effective prevention requires understanding data such as who is at risk and the factors associated with suicide. This fact sheet shares data on the means of carrying out a suicide act, also referred to as mechanisms of…
Released Date:
Injuries are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality among U.S. children and adolescents. State injury and violence prevention programs address a broad range of injury topics across varying populations, with initiatives funded by multiple sources, including federal agencies, hospitals,…
Released Date:
Injuries and violence are leading causes of morbidity and mortality among U.S. children and adolescents. These injuries are preventable. Researchers have identified many strategies that are effective in preventing injuries in this population. This paper synthesizes findings from recent systematic…