CSN Publications
![]() This page displays all Children’s Safety Network (CSN) publications sorted by date released. Please feel free to download and share through Facebook, X, Pinterest, or email.
This page displays all Children’s Safety Network (CSN) publications sorted by date released. Please feel free to download and share through Facebook, X, Pinterest, or email.
Released Date:
In 2019, 4,356 people were killed in crashes involving young drivers (aged 15 - 20). Of these fatalities, 1,603 were young drivers.1 Teenagers contribute to, and suffer from, the consequences of motor vehicle collisions at a disproportionate rate. Teen drivers ages 16 - 19 are nearly three times as…
Read MoreReleased Date:
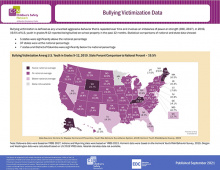
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Bullying Victimization.
Read MoreReleased Date:
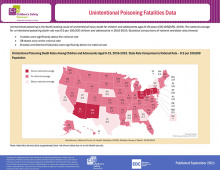
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Unintentional Poisoning Fatalities.
Read MoreReleased Date:
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Adolescent Suicide Deaths.
Read MoreReleased Date:
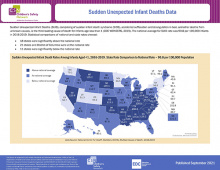
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths.
Read MoreReleased Date:
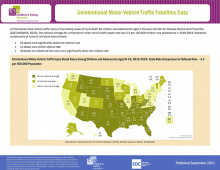
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Unintentional Motor Vehicle Traffic Fatalities.
Read MoreReleased Date:
On average, over 3,000 U.S. children and adolescents die each year from a firearm injury. Approximately nine children and adolescents ages 0 to 19 die by firearm injury each day in the United States, with about five of those deaths being homicide-related and three being suicide-related. In the…
Read MoreReleased Date:
FIREARM SAFETY: Preventing Death by Homicide Firearm homicide is the second leading cause of injury death for children and adolescents ages 0-19. * Approximately nine children and adolescents ages 0 to 19 die by firearm injury each day in the U.S., and about five of those deaths are homicide…
Read MoreReleased Date:
FIREARM SAFETY: Preventing Death by Suicide Firearm suicides are the fourth leading cause of injury death for children ages (10-19).* Approximately nine children and adolescents ages 10 to 19 die by firearm injury each day in the U.S., and about three of those deaths are suicide-related…
Read MoreReleased Date:
The Child Safety Learning Collaborative addresses the leading causes of child and adolescent injuries, fatalities and hospitalizations for youth ages 0-19. This data map provides statistical comparisons of national and state rates for Bullying Victimization, Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths,…
Read MoreReleased Date:
The Planner is for use at the departmental and/or programmatic/work unit level to assess integration of integrative approaches in child safety initiatives. The Planner may be used as a stand-alone tool or with the CSN Framework for Quality Improvement and Innovation in Child Safety: A Guide to…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Suicide is a complex and preventable multi-factor, multi-level health outcome. Effective prevention requires understanding data such as who is at risk and the factors associated with suicide. This fact sheet shares data on the means of carrying out a suicide act, also referred to as mechanisms of…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Numbers Drowning is the leading cause of unintentional injury deaths for children ages 1-4. For children and adolescents ages 5-19, drowning is the third leading cause of unintentional injury deaths. Every year in the U.S., approximately 3,700 people die from unintentional drowning. Nearly 900 of…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Bullying during childhood and adolescence is painful when it happens and can have long lasting effects, both for the bully and the victim. Despite efforts to decrease bullying, the percentage of students reporting being bullied- roughly one in five- has not changed since bullying-related data began…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Child maltreatment (including sexual, physical and emotional abuse) and neglect are serious public health problems which can be prevented. These adverse childhood experiences, resulting in harm, the potential for harm, or threat of harm among children under the age of 18 can be perpetrated by a…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Injuries and violence are leading causes of morbidity and mortality among U.S. children and adolescents. These injuries are preventable. The Children's Safety Now Alliance developed a resource guide, "CSN Framework for Quality Improvement and Innovation in Child Safety: A Guide to Implementing…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Traumatic brain injury (TBI), a condition caused by a bump, blow or jolt to the head which disrupts normal brain function, is a major cause of death and disability in the United States. Nearly 700,000 TBI-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths occur annually in US…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Toy Injuries in U.S. Children: Know the Facts Between 2015 and 2018, U.S. children and adolescents ages 0-19 sustained over 1 million toy-related injuries that were treated in emergency departments. Common injury diagnoses related to toy injuries are laceration, contusion/abrasion, fracture,…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID) refers to the sudden and unexpected death of an infant younger than one year of age. This infographic goes over the definition of SUID, the racial/ethnic differences in SUID rates, risk factors for SUID and provides resources on reducing SUID and…
Read MoreReleased Date:
Injuries are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality among U.S. children and adolescents. State injury and violence prevention programs address a broad range of injury topics across varying populations, with initiatives funded by multiple sources, including federal agencies, hospitals,…
Read More